Difference between revisions of "Rainwater harvesting: Sizing and modeling"
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) |
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) (→Rapid) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{TOClimit|2}} | {{TOClimit|2}} | ||
===Rapid=== | ===Rapid=== | ||
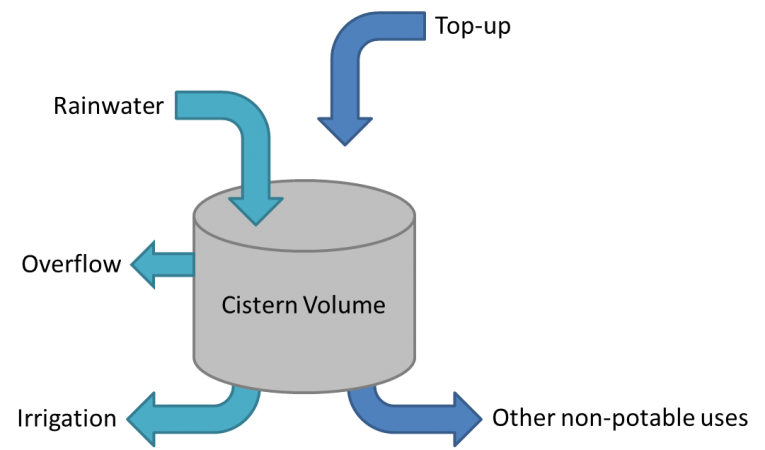
Total cistern volume can be estimated by multiplying the depth of design storm.... | <p>Total cistern volume can be estimated by multiplying the depth of design storm the catchment area. 1 mm of rain over 1 m<sup>2</sup> results in 1 L of runoff. | ||
For example, the 90th percentile event in Barrie is 26 mm, so every 1 m<sup>2</sup> of rooftop will generate 26 L during this storm event. A 2000 m<sup>2</sup> building would generate 54,000 L of runoff. </p> | |||
The designers have three choices:- | |||
<ol> | |||
<li>Construct a suitably sized concrete vault underground to capture all of the water</li> | |||
<li>Alter the slope of the roof to create two or more catchments, the smaller catchments may be diverted to plastic or fiberglass cisterns</li> | |||
<li>Design 1. or 2. Slightly undersized for this storm, but with additional capacity in an infiltration system to capture overflow. Examples include [[Bioretention Cells|bioretention cells]] or [[Infiltration Chambers|infiltration chambers]]. </li> | |||
</ol> | |||
</p> | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="col-md-4"> | <div class="col-md-4"> | ||
Revision as of 20:34, 6 June 2017
Rapid[edit]
Total cistern volume can be estimated by multiplying the depth of design storm the catchment area. 1 mm of rain over 1 m2 results in 1 L of runoff. For example, the 90th percentile event in Barrie is 26 mm, so every 1 m2 of rooftop will generate 26 L during this storm event. A 2000 m2 building would generate 54,000 L of runoff.
The designers have three choices:-
- Construct a suitably sized concrete vault underground to capture all of the water
- Alter the slope of the roof to create two or more catchments, the smaller catchments may be diverted to plastic or fiberglass cisterns
- Design 1. or 2. Slightly undersized for this storm, but with additional capacity in an infiltration system to capture overflow. Examples include bioretention cells or infiltration chambers.
<panelInfo>
</panelInfo>
STEP Rainwater Harvesting Tool[edit]
The Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program have produced a rainwater harvesting design and costing tool specific to Ontario. The tool is in a simple to use Excel format and is free to download.
The Treatment Train Tool[edit]
Once the size of cistern has been determined, it can easily be modelled in many open source and proprietary applications.
In addition to the cistern size, modelling requires
<btnPrimary>The Treatment Train Tool</btnPrimary>