Difference between revisions of "Rainwater harvesting: Sizing and modeling"
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) (→Rapid) |
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) (→Rapid) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
<panelInfo> | <panelInfo> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" widths=300px heights=300px> | <gallery mode="packed" widths=300px heights=300px> | ||
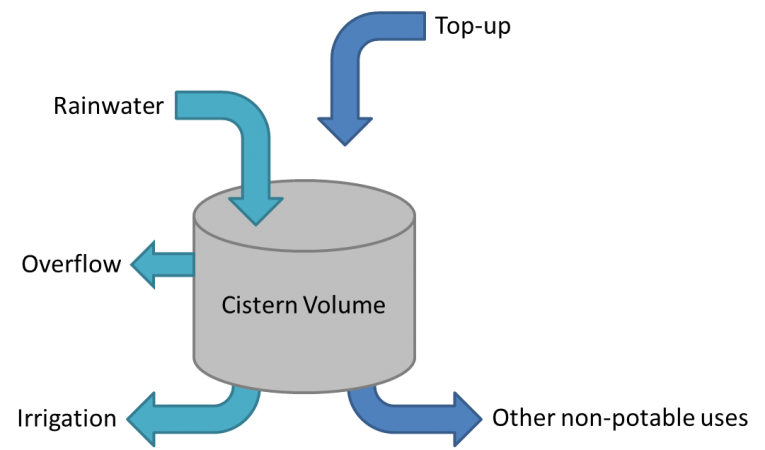
Cistern Size.png| Schematic diagram of the inputs and outputs to a rainwater harvesting cistern | |||
<panelsuccess> | |||
RWH calcs.PNG | RWH calcs.PNG | ||
</panelsuccess> | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</panelInfo> | </panelInfo> | ||
Revision as of 20:51, 26 June 2017
Rapid[edit]
Five percent of the average annual yield (Y0.05, in L) is calculated as the product of:
- The catchment area (A, in m2)
- The runoff coefficient for the catchment (Cvol)
- The average annual rainfall depth (Ra, in mm)
- the efficiency of the pre-storage filter (e), and
- 0.05
Five percent of the average annual demand (D0.05) is calculated as the product of:
- The daily demand per person (Pd, in L)
- The number of occupants (n)
- 365, and
- 0.05
The following calculation is based upon two criteria:
- A design rainfall depth is to be captured entirely by the RWH system.
- The average annual demand (D) is greater than the average annual yield (Y) from the catchment.
When Y0.05/ D0.05 <0.33
The total storage volume required (VS, in L) is calculated as the product of:
- The catchment area (A, in m2)
- The design storm runoff coefficient for the catchment (Cvol)
- The design storm rainfall depth (Rd, in mm), and
- the efficiency of the pre-storage filter (e).
Good catchment selection means that the runoff coefficient (Cvol) should be 0.9 or greater. Filter efficiency can be reasonably estimated as 0.9 pending manufacturer’s information.
When 0.33 < Y0.05/ D0.05 <0.7
The total storage required is the sum of VS and Y0.05.
<panelInfo>
- RWH calcs.PNG
</panelInfo>
STEP Rainwater Harvesting Tool[edit]
The Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program have produced a rainwater harvesting design and costing tool specific to Ontario. The tool is in a simple to use Excel format and is free to download.
In a study of three sites in Ontario, STEP found the annual Cvol of the rooftops to be around 0.8 [1]. This figure includes losses to evaporation, snow being blown off the roof, and number of overflow events.
The Treatment Train Tool[edit]
Once the size of cistern has been determined, it can easily be modelled in many open source and proprietary applications.
In addition to the cistern size, this watershed scale modelling requires input information about draw down. time i.e. the rate of use.
<btnPrimary>The Treatment Train Tool</btnPrimary>
See Also[edit]
This list will be other 'Sizing and Modelling' pages
External Links[edit]
| SEND US YOUR QUESTIONS & FEEDBACK ABOUT THIS PAGE |