Difference between revisions of "Rainwater harvesting: Sizing and modeling"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) |
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
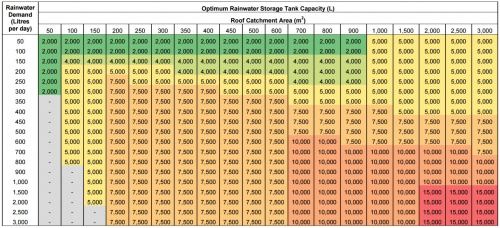
[[File:RWH_tank_capacity_table.jpg|thumb|500 px|Quick reference table generated using STEP RWH tool, (data for the City of Toronto (median annual rainfall 678 mm). Optimal cistern size is that providing at least a 2.5% improvement in water savings following an increase of 1,000 Litres in storage capacity.]] | [[File:RWH_tank_capacity_table.jpg|thumb|500 px|Quick reference table generated using STEP RWH tool, (data for the City of Toronto (median annual rainfall 678 mm). Optimal cistern size is that providing at least a 2.5% improvement in water savings following an increase of 1,000 Litres in storage capacity.]] | ||
The Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program have produced a rainwater harvesting design and costing tool specific to Ontario. The tool is in a simple to use Excel format and is free to download.<br> | The Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program have produced a rainwater harvesting design and costing tool specific to Ontario. The tool is in a simple to use Excel format and is free to download.<br> | ||
{{clickable button|[[Connect the Drops.PNG|link=http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/rainwater-harvesting/rainwater-harvesting-design-and-costing-tool/]]}} | {{clickable button|[[File:Connect the Drops.PNG|link=http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/rainwater-harvesting/rainwater-harvesting-design-and-costing-tool/]]}} | ||
==STEP Treatment Train Tool== | ==STEP Treatment Train Tool== | ||
[[File:TTT.png|400 px|link=http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/low-impact-development-treatment-train-tool/]]<br> | [[File:TTT.png|400 px|link=http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/low-impact-development-treatment-train-tool/]]<br> | ||
'''[[Rainwater harvesting: TTT]]''' | '''[[Rainwater harvesting: TTT]]''' | ||
Revision as of 01:56, 8 September 2017
Simple[edit]
Five percent of the average annual yield can be estimated: $$Y_{0.05} = A \times C_{vol,A}\times R_{a} \times e \times 0.05$$ where:
- Y0.05 = Five percent of the average annual yield (L)
- A = The catchment area (m2)
- Cvol, A = The annual runoff coefficient for the catchment
- Ra = The average annual rainfall depth (mm)
- e = The efficiency of the pre-storage filter
- Filter efficiency (e) can be reasonably estimated as 0.9 pending manufacturer’s information.
- In a study of three sites in Ontario, STEP found the annual Cvol, A of the rooftops to be around 0.8 [1]. This figure includes losses to evaporation, snow being blown off the roof, and a number of overflow events.
Five percent of the average annual demand can be estimated:
$$D_{0.05} = P_{d} \times n\times 18.25$$
Where:
- D0.05 = Five percent of the average annual demand (L)
- Pd = The daily demand per person (L)
- n = The number of occupants
Then the following calculations are based upon two criteria:
- A design rainfall depth is to be captured entirely by the RWH system.
- The average annual demand (D) is greater than the average annual yield (Y) from the catchment.
When \(Y_{0.05}/D_{0.05}<0.33\), the storage volume required can be estimated: Where:
- VS = Storage volume required (L)
- A = The catchment area (m2)
- Cvol,E = The design storm runoff coefficient for the catchment
- Rd = The design storm rainfall depth (mm), and
- e = The efficiency of the pre-storage filter.
- Careful catchment selection means that the runoff coefficient, for a rainstorm event (Cvol, E) should be 0.9 or greater.
Finally, when \(0.33<Y_{0.05}/D_{0.05}<0.7\), the total storage required can be estimated by adding Y0.05:
STEP Rainwater Harvesting Tool[edit]
The Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program have produced a rainwater harvesting design and costing tool specific to Ontario. The tool is in a simple to use Excel format and is free to download.