Difference between revisions of "Green roofs: Performance"
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) m |
Dean Young (talk | contribs) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[File:YorkU2.jpg|thumb|Detail showing the early root development through the mat to the granular planting medium.]] | [[File:YorkU2.jpg|thumb|Detail showing the early root development through the mat to the granular planting medium.]] | ||
Controlled studies have indicated that maturing green roofs may have improved water retention properties <ref>Simon De-Ville, Manoj Menon, Xiaodong Jia, George Reed, Virginia Stovin, The impact of green roof ageing on substrate characteristics and hydrological performance, In Journal of Hydrology, Volume 547, 2017, Pages 332-344, ISSN 0022-1694, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.02.006.</ref>. | |||
The key hydrologic benefit which green roofs have over other forms of LID is the proportion of the water returned to the atmosphere through evapotranspiration. | The key hydrologic benefit which green roofs have over other forms of LID is the proportion of the water returned to the atmosphere through evapotranspiration. | ||
*In Southern Ontario rainwater retention of extensive green roofs without irrigation is between 60% and 70%<ref> | *In Southern Ontario rainwater retention of extensive green roofs without irrigation is between 60% and 70%<ref>Liu, M. Minor, J. 2005. Performance evaluation of an extensive green roof. National Research Council of Canada. NRCC-48204 https://sustainabletechnologies.ca/app/uploads/2013/03/NRC_EastviewGRrept.pdf</ref> <ref name=VS>T. Van Seters, L. Rocha, D. Smith, G. MacMillan; Evaluation of Green Roofs for Runoff Retention, Runoff Quality, and Leachability, Vol. 44 (1): 33 - 47 (2009). Innovative Approaches to Stormwater Management in Canada</ref> <ref name=Hill>Hill J, Drake J, Sleep B, Margolis L. Influences of Four Extensive Green Roof Design Variables on Stormwater Hydrology. J Hydrol Eng. 2017;22(8):04017019. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001534</ref>. | ||
*Including winter periods with snow accumulation and thaw, the annual retention of extensive green roofs is around 50% <ref | *Including winter periods with snow accumulation and thaw, the annual retention of extensive green roofs is around 50% <ref name=VS/><ref name=Hill/>. | ||
*Using a compost based planting medium improves retention by around 10% i.e. 60 % for compost compared to 50% for granular. | *Using a compost based planting medium improves retention by around 10% i.e. 60 % for compost compared to 50% for granular. | ||
*Daily irrigation can reduce the annual retention by 20% compared to a roof without irrigation. i.e. 40% for irrigated compared to 60% without irrigation<ref name=Hill/>. However, recirculating rainwater from a cistern was estimated to double the annual retention in Florida<ref>http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/4/4/914</ref>. The research team modeled 87% retention for a green roof coupled with a cistern, compared to 43% for the green roof alone. | *Daily irrigation can reduce the annual retention by 20% compared to a roof without irrigation. i.e. 40% for irrigated compared to 60% without irrigation<ref name=Hill/>. However, recirculating rainwater from a cistern was estimated to double the annual retention in Florida<ref>Hardin, M.; Wanielista, M.; Chopra, M. A Mass Balance Model for Designing Green Roof Systems that Incorporate a Cistern for Re-Use. Water 2012, 4, 914-931. http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/4/4/914</ref>. The research team modeled 87% retention for a green roof coupled with a cistern, compared to 43% for the green roof alone. | ||
An appropriate NRCS curve numbers for green roofs without irrigation in Southern Ontario is 90 <ref>Curve Number and Runoff Coefficients for Extensive Living Roofs | An appropriate NRCS curve numbers for green roofs without irrigation in Southern Ontario is 90 <ref>Curve Number and Runoff Coefficients for Extensive Living Roofs | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
===Water quality=== | ===Water quality=== | ||
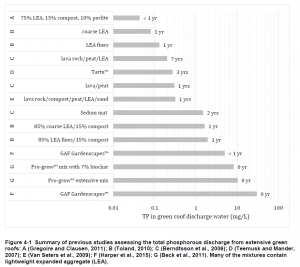
Many green roofs receive only rainwater, which is relatively | Many green roofs receive only rainwater, which is relatively free of contaminants like nutrients and heavy metals, but can contribute contaminants to roof runoff, most notably through leaching of [[Nutrients]] from the growing medium substrate during early establishment.<ref>Vijayaraghavan, K., Harkishore Kumar Reddy, D., Yun, Y. 2018. Improving the quality of runoff from green roofs through synergistic biosorption and phytoremediation techniques: A review. Sustainable Cities and Society. 46 (2019) 101381. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2210670718319383?via%3Dihub</ref> Reported concentrations of Total [[Phosphorus]] in green roof runoff have been observed to vary from less than 0.1 ppm to over 10 ppm.<ref>Hill J., Drake J., Sleep B., Margolis L. 2017. Influences of Four Extensive Green Roof Design Variables on Stormwater Hydrology. J Hydrol Eng. 2017;22(8):04017019. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001534</ref>. To improve the quality of runoff from green roofs, Vijayaraghavan et al. (2018) recommend considering the sorption capacity of the growing medium substrate, the phytoremediation potential of plants and incorporation of sorbent [[Additives]] to growing medium substrates.<ref>Vijayaraghavan, K., Harkishore Kumar Reddy, D., Yun, Y. 2018. Improving the quality of runoff from green roofs through synergistic biosorption and phytoremediation techniques: A review. Sustainable Cities and Society. 46 (2019) 101381. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2210670718319383?via%3Dihub</ref> | ||
A 'closed loop' system can be created by coupling a rainwater harvesting system | In dense urban centres, green roofs are increasingly being used to receive irrigation from harvested rainwater. Current Ontario Building Code permits the use of rooftop runoff for landscape irrigation purposes, so long as it is 'free of solids'. | ||
A 'closed loop' system can be created by coupling a rainwater harvesting system with a green roof and harvesting and reusing roof runoff as a source of water for irrigation during dry periods, so the only water leaving the system is through evapotranspiration. This can prevent runoff from leaving the site and thereby prevent contaminant loading to the environment. | |||
[[File:TP.PNG|thumb|Total phosphorous concentrations reported in green roof runoff(abstracted from Hill 2017)]] | [[File:TP.PNG|thumb|Total phosphorous concentrations reported in green roof runoff(abstracted from Hill 2017)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:02, 20 March 2023
Controlled studies have indicated that maturing green roofs may have improved water retention properties [1].
The key hydrologic benefit which green roofs have over other forms of LID is the proportion of the water returned to the atmosphere through evapotranspiration.
- In Southern Ontario rainwater retention of extensive green roofs without irrigation is between 60% and 70%[2] [3] [4].
- Including winter periods with snow accumulation and thaw, the annual retention of extensive green roofs is around 50% [3][4].
- Using a compost based planting medium improves retention by around 10% i.e. 60 % for compost compared to 50% for granular.
- Daily irrigation can reduce the annual retention by 20% compared to a roof without irrigation. i.e. 40% for irrigated compared to 60% without irrigation[4]. However, recirculating rainwater from a cistern was estimated to double the annual retention in Florida[5]. The research team modeled 87% retention for a green roof coupled with a cistern, compared to 43% for the green roof alone.
An appropriate NRCS curve numbers for green roofs without irrigation in Southern Ontario is 90 [6][4].
Water quality[edit]
Many green roofs receive only rainwater, which is relatively free of contaminants like nutrients and heavy metals, but can contribute contaminants to roof runoff, most notably through leaching of Nutrients from the growing medium substrate during early establishment.[7] Reported concentrations of Total Phosphorus in green roof runoff have been observed to vary from less than 0.1 ppm to over 10 ppm.[8]. To improve the quality of runoff from green roofs, Vijayaraghavan et al. (2018) recommend considering the sorption capacity of the growing medium substrate, the phytoremediation potential of plants and incorporation of sorbent Additives to growing medium substrates.[9]
In dense urban centres, green roofs are increasingly being used to receive irrigation from harvested rainwater. Current Ontario Building Code permits the use of rooftop runoff for landscape irrigation purposes, so long as it is 'free of solids'. A 'closed loop' system can be created by coupling a rainwater harvesting system with a green roof and harvesting and reusing roof runoff as a source of water for irrigation during dry periods, so the only water leaving the system is through evapotranspiration. This can prevent runoff from leaving the site and thereby prevent contaminant loading to the environment.
- ↑ Simon De-Ville, Manoj Menon, Xiaodong Jia, George Reed, Virginia Stovin, The impact of green roof ageing on substrate characteristics and hydrological performance, In Journal of Hydrology, Volume 547, 2017, Pages 332-344, ISSN 0022-1694, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.02.006.
- ↑ Liu, M. Minor, J. 2005. Performance evaluation of an extensive green roof. National Research Council of Canada. NRCC-48204 https://sustainabletechnologies.ca/app/uploads/2013/03/NRC_EastviewGRrept.pdf
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 T. Van Seters, L. Rocha, D. Smith, G. MacMillan; Evaluation of Green Roofs for Runoff Retention, Runoff Quality, and Leachability, Vol. 44 (1): 33 - 47 (2009). Innovative Approaches to Stormwater Management in Canada
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Hill J, Drake J, Sleep B, Margolis L. Influences of Four Extensive Green Roof Design Variables on Stormwater Hydrology. J Hydrol Eng. 2017;22(8):04017019. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001534
- ↑ Hardin, M.; Wanielista, M.; Chopra, M. A Mass Balance Model for Designing Green Roof Systems that Incorporate a Cistern for Re-Use. Water 2012, 4, 914-931. http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/4/4/914
- ↑ Curve Number and Runoff Coefficients for Extensive Living Roofs Elizabeth Fassman-Beck, Ph.D., A.M.ASCE; William Hunt, Ph.D., P.E., M.ASCE; Robert Berghage, Ph.D.; Donald Carpenter, Ph.D., P.E., M.ASCE; Timothy Kurtz, P.E., M.ASCE; Virginia Stovin, Ph.D.; and Bridget Wadzuk, Ph.D., A.M.ASCE
- ↑ Vijayaraghavan, K., Harkishore Kumar Reddy, D., Yun, Y. 2018. Improving the quality of runoff from green roofs through synergistic biosorption and phytoremediation techniques: A review. Sustainable Cities and Society. 46 (2019) 101381. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2210670718319383?via%3Dihub
- ↑ Hill J., Drake J., Sleep B., Margolis L. 2017. Influences of Four Extensive Green Roof Design Variables on Stormwater Hydrology. J Hydrol Eng. 2017;22(8):04017019. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001534
- ↑ Vijayaraghavan, K., Harkishore Kumar Reddy, D., Yun, Y. 2018. Improving the quality of runoff from green roofs through synergistic biosorption and phytoremediation techniques: A review. Sustainable Cities and Society. 46 (2019) 101381. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2210670718319383?via%3Dihub