Difference between revisions of "Screening LID options"
Kyle menken (talk | contribs) |
Tvanseters (talk | contribs) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOClimit|2}} | {{TOClimit|2}} | ||
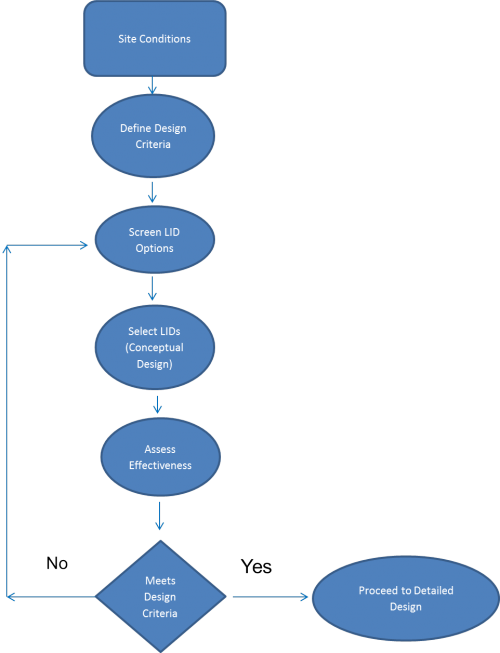
[[File:Screeningprocessdiagram.png|thumb|500 px|Process Diagram for Screening LID Options]] | |||
== Process for selecting an individual or suite of LID Options == | == Process for selecting an individual or suite of LID Options == | ||
This guidance article intends to help reduce the number of LID options in the preliminary phases of design and to alert the designer to LID opportunities unique to the site-type being assessed. When going through the process of screening LID options, it is important to have a larger contextual understanding of [[Integrated water management]], [[Site design strategies]], [[Siting and layout of development | This guidance article intends to help reduce the number of LID options in the preliminary phases of design and to alert the designer to LID opportunities unique to the site-type being assessed. When going through the process of screening LID options, it is important to have a larger contextual understanding of [[Integrated water management]], [[Site design strategies]], and [[Siting and layout of development]]. | ||
== Site Conditions == | == Site Conditions == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
The design criteria required to protect, enhance or restore the environmental resources can be grouped under the following five categories: | The design criteria required to protect, enhance or restore the environmental resources can be grouped under the following five categories: | ||
* Flood | *[[Flood control]] | ||
* Water quality | *[[Water quality]] | ||
* Erosion control | *Erosion control | ||
* Groundwater recharge | *[[Groundwater|Groundwater recharge]] | ||
* Natural heritage systems or | *Natural heritage systems or other types of green infrastructure | ||
== Screen potential LID options == | == Screen potential LID options == | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
When working in retrofit scenarios, note that each particular land-use type - road ROWs, residential, industrial, commercial, institutional, and park lands - all provide unique opportunities and challenges: | When working in retrofit scenarios, note that each particular land-use type - road ROWs, residential, industrial, commercial, institutional, and park lands - all provide unique opportunities and challenges: | ||
*[[LID opportunities | *[[LID opportunities in road-right-of-ways]] | ||
*[[LID opportunities in residential types]] | *[[LID opportunities in residential types]] | ||
*[[LID | *[[LID opportunities in industrial, commercial and multi-residential types]] | ||
*[[LID opportunities in | *[[LID opportunities in public lands]] | ||
===Performance requirements=== | ===Performance requirements=== | ||
Resources for evaluating LID practices within Ontario can be found at [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/ Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program (STEP)] and [http://www.creditvalleyca.ca/low-impact-development/lid-maintenance-monitoring/lid-monitoring-sites/ Credit Valley Conservation's LID Monitoring program]. For a global perspective on LID performance across various geographical regions, check out the [http://www.bmpdatabase.org/index.htm International Stormwater BMP Database]. Performance data can be downloaded or uploaded and statistical analysis tools are provided. | Resources for evaluating LID practices within Ontario can be found at [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/ Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program (STEP)] and [http://www.creditvalleyca.ca/low-impact-development/lid-maintenance-monitoring/lid-monitoring-sites/ Credit Valley Conservation's LID Monitoring program]. For a global perspective on LID performance across various geographical regions, check out the [http://www.bmpdatabase.org/index.htm International Stormwater BMP Database]. Performance data can be downloaded or uploaded and statistical analysis tools are provided. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
=== Life cycle costing=== | === Life cycle costing=== | ||
See [[Cost analysis resources]] | |||
===Assessing effectiveness=== | |||
{{:LIDTTT}} | |||
After selecting a suite of BMPs and running the models, make a comparison between the modelling results results and the environmental design criteria. Employ an iterative approach, which involves adjusting the size or adding/deleting BMPs until the environmental design criteria are met. The LIDTTT can help with adjusting the size of the features to meet design criteria. Once met, the project can proceed to the detailed design stage. | |||
---- | |||
After selecting a suite of BMPs and running the models, make a comparison between the modelling results results and the environmental design criteria. Employ | |||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 19 November 2019
Process for selecting an individual or suite of LID Options[edit]
This guidance article intends to help reduce the number of LID options in the preliminary phases of design and to alert the designer to LID opportunities unique to the site-type being assessed. When going through the process of screening LID options, it is important to have a larger contextual understanding of Integrated water management, Site design strategies, and Siting and layout of development.
Site Conditions[edit]
Complete definition of pre-development site conditions is essential prior to screening of potential stormwater BMPs. The designer should prepare maps describing site conditions and identifying all environmental features and functions that need consideration in accordance with provincial, municipal and conservation authority development regulations. This includes watercourses and small drainage features, floodplains, important recharge areas, steep slopes, wetlands, natural heritage conservation areas and significant wildlife habitats. In addition, information regarding native soil types, infiltration capacity and depth to water table must be determined.
In retrofit scenarios, site conditions will vary and maps can be explicit with land-use type. Road right of ways, parks, residential, industrial, commercial and/or institutional should be noted.
For additional information on site conditions to note for:
- Road right of way retrofits, see Site Conditions Road Right of Ways
- Public lands including parks, churches, or schools, see Public Lands Site Conditions
- Commercial, industrial and multi-residential, see Site Conditions Commercial, Industrial, and Multi-Residential
- Residential, see Site Conditions Residential
Define design criteria[edit]
Design criteria should be required to:
- Preserve groundwater and baseflow characteristics
- Prevent undesirable and costly geomorphic changes in the watercourse
- Prevent any increases in flood risk potential
- Protect water quality
- Maintain an appropriate diversity of aquatic life and opportunities for human uses
The design criteria required to protect, enhance or restore the environmental resources can be grouped under the following five categories:
- Flood control
- Water quality
- Erosion control
- Groundwater recharge
- Natural heritage systems or other types of green infrastructure
Screen potential LID options[edit]
Site constraints[edit]
When attempting to apply stormwater BMPs within a development site, give careful consideration to site conditions and constraints. See this handy table for and outline of the factors constraining the use of each LID BMP. Further information regarding constraints to the design of various end-of-pipe BMPs can be found in the Ontario Ministry of the Environment Stormwater Management Planning and Design Manual (2003). Before resorting to end-of-pipe BMPs, evaluate whether LID BMPs can meet the design criteria.
LID opportunities and land use types[edit]
When working in retrofit scenarios, note that each particular land-use type - road ROWs, residential, industrial, commercial, institutional, and park lands - all provide unique opportunities and challenges:
Performance requirements[edit]
Resources for evaluating LID practices within Ontario can be found at Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program (STEP) and Credit Valley Conservation's LID Monitoring program. For a global perspective on LID performance across various geographical regions, check out the International Stormwater BMP Database. Performance data can be downloaded or uploaded and statistical analysis tools are provided.
Operations and maintenance requirements[edit]
The LID Inspection and Maintenance Guide is intended to assist municipalities and industrial/commercial/institutional (ICI) property managers with developing their capacity to integrate LID BMPs into their stormwater infrastructure programs. Part 1 of the document provides guidance on designing an effective LID BMP inspection and maintenance program, based on experiences and advice from leading jurisdictions in the United States, adapted to an Ontario context. Part 2 of the document establishes standard cold climate protocols for inspection, testing and maintenance of seven types of structural LID BMPs.
Life cycle costing[edit]
Assessing effectiveness[edit]
Overview[edit]
The Low Impact Development Treatment Train Tool (LID TTT) is designed to help developers, consultants, municipalities and landowners understand and implement more sustainable stormwater management planning and design practices in their watersheds.
The LID TTT focuses on the use of Low Impact Development best management practices (BMPs) to meet stormwater management criteria for the site and can be used to:
- analyze annual and event based runoff volumes,
- including water budget information: surface evapotranspiration, surface runoff, and infiltration to soil
- provide estimates of water quality improvements.
The LID TTT is built upon the open source EPA SWMM5 hydrologic model providing a user-friendly interface for novice modelers and cross-compatibility with SWMM5 for further model development.
The LID TTT has been developed in partnership between Lake Simcoe Region Conservation Authority, Credit Valley Conservation, and Toronto and Region Conservation Authority.
Integration with this guide is through suggested 'starting point' values for design parameters for the following BMP types:
- Bioretention
- Vegetated filter strips
- Infiltration trenches
- Permeable pavements
- Rainwater harvesting
- Swales
- Dry ponds
This links to the project page, where you can download your free copy of the LID TTT.
How to download & install the Tool[edit]
View the Step-by-step instructional video below on how to download and install the LID TTT. This video covers how to set up your model, add LIDs and analyze results for pre- to post-development scenario
<iframe width="" height="" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/?listType=playlist&list=" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
How to use the Tool[edit]
View the Step-by-step instructional video below on how to use the LID TTT for you LID BMP projects.
<iframe width="" height="" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/?listType=playlist&list=" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
How to size your LID using an I:P ratio[edit]
View the Step-by-step instructional video below on how to use the LID TTT to route a simple residential sub-catchment to a bioswale feature, and shows users to consider the Impervious to pervious (or I:P) ratio in sizing the LID.
<iframe width="" height="" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/?listType=playlist&list=" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
After selecting a suite of BMPs and running the models, make a comparison between the modelling results results and the environmental design criteria. Employ an iterative approach, which involves adjusting the size or adding/deleting BMPs until the environmental design criteria are met. The LIDTTT can help with adjusting the size of the features to meet design criteria. Once met, the project can proceed to the detailed design stage.