Difference between revisions of "Screening LID options"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The guidance found on this page is not intended be prohibitive of LID options, but rather to help reduce the number of LID options in the preliminary phases of design and alert the designer to LID opportunities unique to the site being assessed. When going through the process of screening LID options, it is important to have a larger contextual understanding of [[Integrated water management]], [[Site design strategies]], [[Siting and layout of development]], and [[Link title]]. | The guidance found on this page is not intended be prohibitive of LID options, but rather to help reduce the number of LID options in the preliminary phases of design and alert the designer to LID opportunities unique to the site being assessed. When going through the process of screening LID options, it is important to have a larger contextual understanding of [[Integrated water management]], [[Site design strategies]], [[Siting and layout of development]], and [[Link title]]. | ||
== Site Conditions == | |||
Complete definition of pre-development site conditions is essential prior to screening of | Complete definition of pre-development site conditions is essential prior to screening of potential stormwater BMPs. The designer should prepare maps describing site | ||
conditions to ensure that all environmental features and functions that need consideration in accordance with provincial, municipal and conservation authority | |||
development regulations are identified. This includes watercourses and small drainage features, floodplains, important recharge areas, steep slopes, wetlands, natural heritage | |||
conservation areas and significant wildlife habitats. In addition, information regarding native soil types, infiltration capacity and depth to water table must be determined. | |||
conservation areas and significant wildlife habitats. In addition, information regarding | |||
native soil types, infiltration capacity and depth to water table must be determined. | |||
| Line 31: | Line 23: | ||
* residential, see [[Site Conditions Residential]] | * residential, see [[Site Conditions Residential]] | ||
== Define Design Criteria == | |||
respective CVC and TRCA Stormwater Management Criteria documents. If outside jurisdictional | A detailed description of the design criteria that need to be defined is provided in the respective CVC and TRCA Stormwater Management Criteria documents. If outside jurisdictional | ||
boundaries, criteria developed should have requirements to: | boundaries, criteria developed should have requirements to: | ||
| Line 45: | Line 35: | ||
* maintain an appropriate diversity of aquatic life and opportunities for human uses | * maintain an appropriate diversity of aquatic life and opportunities for human uses | ||
The design criteria required to protect, enhance or restore the environmental resources | The design criteria required to protect, enhance or restore the environmental resources can be grouped under the following five categories. | ||
can be grouped under the following five categories. | |||
* Flood Protection; | * Flood Protection; | ||
| Line 56: | Line 44: | ||
== Screen Potential LID Options == | |||
A number of factors need to be considered when screening the suitability of a given location within a development site for application of stormwater BMPs. Table 3.4.1 | |||
summarizes site constraints associated with some general types of structural LID practices for stormwater management that should be considered. Further | |||
information regarding constraints to the design of various end-of-pipe BMPs can be found in the Ontario Ministry of the Environment Stormwater Management Planning and | |||
design criteria before the use of end-of-pipe BMPs. | Design Manual (2003). The use of LID BMPs should be considered first to meet the design criteria before the use of end-of-pipe BMPs. | ||
=== Structural Requirements or Site Constraints === | |||
[[LID Site Criteria and Constraints]] | [[LID Site Criteria and Constraints]] | ||
=== Performance Requirements === | |||
For additional resources on LID performance studies, please click on [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/ LID Performance Reports] | For additional resources on LID performance studies, please click on [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/ LID Performance Reports] | ||
=== Operations and Maintenance Requirements === | |||
[http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/low-impact-development-stormwater-practice-inspection-and-maintenance-guide/ LID Inspection and Maintenance Guide] | [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/low-impact-development-stormwater-practice-inspection-and-maintenance-guide/ LID Inspection and Maintenance Guide] | ||
=== Life Cycle Costing Requirements === | |||
[http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/low-impact-development-life-cycle-costs/ LID Life Cycle Costing Tool] | [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/low-impact-development-life-cycle-costs/ LID Life Cycle Costing Tool] | ||
== Select LIDs (Conceptual Design) == | |||
In order to assess if the selected suite of BMPs effectively meet the design criteria | In order to assess if the selected suite of BMPs effectively meet the design criteria either computer models or simple spreadsheet models should be used. Model selection | ||
will be based on the size and type of development. A wide range of simple to complex computer models such as Visual OTTHYMO, SWMM, SWMMHYNO, HSP-F andQUALHYMO are available. | |||
The Low Impact Development Treatment Train Tool (LID TTT) has been developed by Lake Simcoe Region Conservation Authority (LSRCA), Credit Valley Conservation (CVC) and Toronto and Region Conservation Authority (TRCA) as a | |||
tool to help developers, consultants, municipalities and landowners understand and implement more sustainable stormwater management planning and design practices in their watersheds. The purpose of the tool is to analyze | |||
annual and event based runoff volumes and pollutant load removal by the use of Best Management Practices (BMP)’s and Low Impact Development (LID) techniques. The LID TTT provides preliminary water budget analysis (i.e. | |||
surface ET, surface runoff, infiltration to soil) and pollutant load removal estimates for pre- and post-development scenarios. The tool is built upon the open source EPA SWMM5 model providing a user-friendly interface for | |||
novice modelers and cross-compatibility with SWMM5 for further model development. To download the beta version, please click [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/low-impact-development-treatment-train-tool/ LID | |||
Treatment Train Tool] | |||
== Assess Effectiveness == | |||
Once the suite of best management practices have been selected and the models have been run, a comparison of the results and the environmental design criteria can be made. An iterative approach, which involves adjusting the | |||
proceed to the detailed design stage. | size or adding/deleting BMPs should be used until the environmental design criteria are met. The project can then proceed to the detailed design stage. | ||
Revision as of 18:01, 20 September 2017
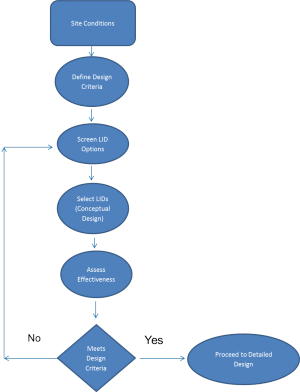
Process for selecting an individual or suite of LID Options[edit]
The guidance found on this page is not intended be prohibitive of LID options, but rather to help reduce the number of LID options in the preliminary phases of design and alert the designer to LID opportunities unique to the site being assessed. When going through the process of screening LID options, it is important to have a larger contextual understanding of Integrated water management, Site design strategies, Siting and layout of development, and Link title.
Site Conditions[edit]
Complete definition of pre-development site conditions is essential prior to screening of potential stormwater BMPs. The designer should prepare maps describing site
conditions to ensure that all environmental features and functions that need consideration in accordance with provincial, municipal and conservation authority
development regulations are identified. This includes watercourses and small drainage features, floodplains, important recharge areas, steep slopes, wetlands, natural heritage
conservation areas and significant wildlife habitats. In addition, information regarding native soil types, infiltration capacity and depth to water table must be determined.
In retrofit scenarios, site conditions will vary and can be explicit with land use type such as road right of ways, parks, residential, industrial, commercial and/or institutional should be noted.
For additional information on site conditions to note for:
- road right of way retrofits, see Site Conditions Road Right of Ways
- public lands including parks, churches, or schools, see Public Lands Site Conditions
- commercial, industrial and multi-residential, see Site Conditions Commercial, Industrial, and Multi-Residential
- residential, see Site Conditions Residential
Define Design Criteria[edit]
A detailed description of the design criteria that need to be defined is provided in the respective CVC and TRCA Stormwater Management Criteria documents. If outside jurisdictional
boundaries, criteria developed should have requirements to:
- preserve groundwater and baseflow characteristics;
- prevent undesirable and costly geomorphic changes in the watercourse;
- prevent any increases in flood risk potential;
- protect water quality; and ultimately,
- maintain an appropriate diversity of aquatic life and opportunities for human uses
The design criteria required to protect, enhance or restore the environmental resources can be grouped under the following five categories.
- Flood Protection;
- Water Quality;
- Erosion Control;
- Recharge; and
- Natural Heritage Systems or green infrastructure
Screen Potential LID Options[edit]
A number of factors need to be considered when screening the suitability of a given location within a development site for application of stormwater BMPs. Table 3.4.1
summarizes site constraints associated with some general types of structural LID practices for stormwater management that should be considered. Further
information regarding constraints to the design of various end-of-pipe BMPs can be found in the Ontario Ministry of the Environment Stormwater Management Planning and
Design Manual (2003). The use of LID BMPs should be considered first to meet the design criteria before the use of end-of-pipe BMPs.
Structural Requirements or Site Constraints[edit]
LID Site Criteria and Constraints
Performance Requirements[edit]
For additional resources on LID performance studies, please click on LID Performance Reports
Operations and Maintenance Requirements[edit]
LID Inspection and Maintenance Guide
Life Cycle Costing Requirements[edit]
Select LIDs (Conceptual Design)[edit]
In order to assess if the selected suite of BMPs effectively meet the design criteria either computer models or simple spreadsheet models should be used. Model selection
will be based on the size and type of development. A wide range of simple to complex computer models such as Visual OTTHYMO, SWMM, SWMMHYNO, HSP-F andQUALHYMO are available.
The Low Impact Development Treatment Train Tool (LID TTT) has been developed by Lake Simcoe Region Conservation Authority (LSRCA), Credit Valley Conservation (CVC) and Toronto and Region Conservation Authority (TRCA) as a
tool to help developers, consultants, municipalities and landowners understand and implement more sustainable stormwater management planning and design practices in their watersheds. The purpose of the tool is to analyze
annual and event based runoff volumes and pollutant load removal by the use of Best Management Practices (BMP)’s and Low Impact Development (LID) techniques. The LID TTT provides preliminary water budget analysis (i.e.
surface ET, surface runoff, infiltration to soil) and pollutant load removal estimates for pre- and post-development scenarios. The tool is built upon the open source EPA SWMM5 model providing a user-friendly interface for
novice modelers and cross-compatibility with SWMM5 for further model development. To download the beta version, please click [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/low-impact-development-treatment-train-tool/ LID
Treatment Train Tool]
Assess Effectiveness[edit]
Once the suite of best management practices have been selected and the models have been run, a comparison of the results and the environmental design criteria can be made. An iterative approach, which involves adjusting the
size or adding/deleting BMPs should be used until the environmental design criteria are met. The project can then proceed to the detailed design stage.