Difference between revisions of "Jar test"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) m |
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Specifying that [[aggregates]] for the construction of LID practices must be free from fines is important. | Specifying that [[aggregates]] for the construction of LID practices must be free from fines is important. | ||
But checking that the delivered materials meet specification is essential to reduce problems with construction and longer term performance. | But checking that the delivered materials meet specification is essential to reduce problems with construction and longer term performance. | ||
When possible, Construction Managers should observe the offloading of materials to watch for dust clouds. Aggregates or [[sand]] for LID construction should not give rise to clouds of dust when dumped. | When possible, Construction Managers should observe the offloading of materials to watch for dust clouds. Aggregates or [[sand]] for LID construction should not give rise to clouds of dust when dumped. | ||
Revision as of 19:16, 12 June 2018
Specifying that aggregates for the construction of LID practices must be free from fines is important. But checking that the delivered materials meet specification is essential to reduce problems with construction and longer term performance.
When possible, Construction Managers should observe the offloading of materials to watch for dust clouds. Aggregates or sand for LID construction should not give rise to clouds of dust when dumped.
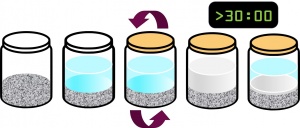
A simple jar test can be used to gauge the proportion of fines in an aggregate product before acceptance. Apparatus:
- A large wide-mouthed jar - glass or clear plastic are both fine.
- Tap water, and
- The aggregate to be tested.
Method:
- Collect approximately 5 cm of material in the jar (or at least two complete layers of 40 mm clear stone),
- Add water to around 3/4 full,
- Secure cap and shake,
- Leave for at least 30 minutes and until the water is clear - plan to run the test overnight when possible,
- Examine the layer of sediment - if > 3 mm has been washed from 5 cm of product, reject the material,
Note that the sediment may collect on top of, or at the bottom of the construction material.
External references[edit]
- Heger, S. (2014). Critical Aspects During System Installation and Inspection General equipment considerations. In PMSA conference. Retrieved from http://www.psma.net/pdf/14/conference-presentations/Keys_to_Installation_(Heger).pdf
- Manitoba. (2010). Onsite Wastewater Management Systems: Field Reference Guide - JAR TEST. Retrieved from http://www.gov.mb.ca/sd/envprograms/wastewater/pdf/jar_test_reference_03_2010.pdf