Difference between revisions of "Infiltration chambers"
Dean Young (talk | contribs) |
Dean Young (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
*Structurally reinforced chambers, vaults, crates, perforated pipes or other void-forming structures; | *Structurally reinforced chambers, vaults, crates, perforated pipes or other void-forming structures; | ||
*[[Reservoir_gravel|Coarse aggregate]] to embed the void-forming structures and temporarily store water; | *[[Reservoir_gravel|Coarse aggregate]] to embed the void-forming structures and temporarily store water; | ||
*[[Pipes| | *[[Pipes|Pipes]] to convey water into and out of the practice; and | ||
*[[Geotextiles]] to maintain separation between the storage reservoir and surrounding native soil. | *[[Geotextiles]] to maintain separation between the storage reservoir and surrounding native soil. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! rowspan="2"|System type | ! rowspan="2"|System type | ||
! | ! Perforated pipes | ||
! Vaults | ! Vaults | ||
! Arched chambers | ! Arched chambers | ||
Revision as of 18:01, 27 July 2020
Overview[edit]
As their name suggests infiltration chambers work exclusively to infiltrate stormwater. They are an underground facility and are often used beneath parking lots or playing fields to treat flow routed from other areas.
Infiltration chambers are an ideal technology for:
- Installing below any type of surface or landscape
- Receiving and infiltrating large volumes of water
The fundamental components of an infiltration chamber system are:
- Pretreatment devices to retain trash, debris, sediment and floatables and prevent clogging of inlets, underlying native soil and outlets;
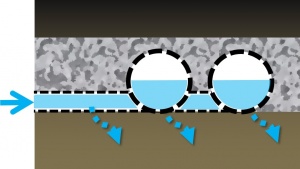
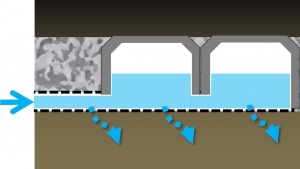
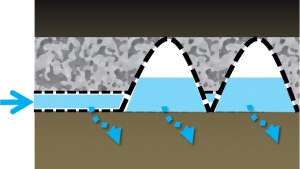
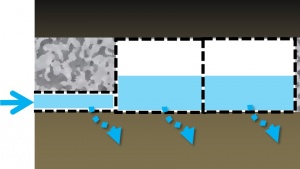
- Structurally reinforced chambers, vaults, crates, perforated pipes or other void-forming structures;
- Coarse aggregate to embed the void-forming structures and temporarily store water;
- Pipes to convey water into and out of the practice; and
- Geotextiles to maintain separation between the storage reservoir and surrounding native soil.
Planning Considerations[edit]
All types of modular systems require a bedding of angular clear stone to permit infiltration, and provide a foundation for the installation:
- Plastic modules usually have a parabolic shape to support the load above. The spaces between the rows of modules are filled with clear stone to support overlying structures.
- Concrete vaults are often rectangular-shaped and can, in some circumstances, be employed without any additional cover. However, a minimum of 20 cm cover is recommended for most applications. Where this cover is planting soil this can support turf grass. Greater planting soil depths are required to support more deeply rooting plants like perennials and shrubs (45 to 60 cm) and trees (85 to 100 cm).
Design[edit]
Sizing[edit]
Infiltration: Sizing and modeling
Modeling[edit]
Materials[edit]
Chambers[edit]
Plastic chambers[edit]
Chambers should be compliant with:
- CSA B184-17 "Polymeric subsurface stormwater management structures".
- ASTM F2418-16a “Standard Specification for Polypropylene (PP) Corrugated Wall Stormwater Collection Chambers”.
Allowable loads for the chambers must be determined in accordance with ASTM F2787-13 “Standard Practice for Structural Design of Thermoplastic Corrugated Wall Stormwater Collection Chambers”.
Concrete vaults[edit]
Concrete vault-type systems should be compliant with:
- CSA A23.3-14 "Design of concrete structures",
- CSA A23.1-09/A23.2-09 (R2014) "Concrete materials and methods of concrete construction/Test methods and standard practices for concrete", and
- ASTM C858 - 10e1 "Standard Specification for Underground Precast Concrete Utility Structures".
Aggregates[edit]
This article gives recommendations for aggregate to be used to store water for infiltration. This is usually called 'clear stone' at aggregate yards.
To see an analysis of Ontario Standard Specifications for granular materials, see OPSS aggregates.
For advice on decorative surface aggregates see Stone
Gravel used for underdrains in bioretention, infiltration trenches and chambers, and exfiltration trenches should be 20 or 50 mm, uniformly-graded, clean (maximum wash loss of 0.5%), crushed angular stone that has a porosity of 0.4[1].
The clean wash to prevent rapid accumulation of fines from the aggregate particles in the base of the reservoir. The uniform grading and the angularity are important to maintain pore throats and clear voids between particles. (i.e. achieve the porosity). Porosity and permeability are directly influenced by the size, gradation and angularity of the particles [2]. See jar test for on-site verification testing protocols.
Gravel with structural requirements should also meet the following criteria:
- Minimum durability index of 35
- Maximum abrasion of 10% for 100 revolutions and maximum of 50% for 500 revolutions
Standard specifications for the gradation of aggregates are maintained by ASTM D2940
The highest porosity is found in uniformly graded aggregate, as there are no smaller particles to occupy the inter-particle pores. [2]
Higher permeability is found in larger, angular, uniformly graded aggregate. This is due to larger pore sizes and lower tortuosity. [2]
Other[edit]
Construction[edit]
Gallery[edit]
Infiltration chambers being installed.
Parking lot stormwater detention system, partially installed. Photo credit: Arbitrarily0
Contractors construct an underground soakaway on the runway extension of Taxiway Alpha as shown here Oct. 5, 2012, at RAF Mildenhall, England. Photo credit: Karen Abeyasekere
Infiltration chambers being installed.
Example of "crate style" Infiltration chambers being installed in East Gwillimbury. Photo credit: Make-Way Environmental Technologies Inc.
External links[edit]
In our effort to make this guide as functional as possible, we have decided to include proprietary systems and links to manufacturers websites.
Inclusion of such links does not constitute endorsement by the Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program.
Lists are ordered alphabetically; link updates are welcomed using the form below.
Plastic chambers[edit]
Concrete chambers[edit]
- ↑ Porosity of Structural Backfill, Tech Sheet #1, Stormtech, Nov 2012, http://www.stormtech.com/download_files/pdf/techsheet1.pdf accessed 16 October 2017
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Judge, Aaron, "Measurement of the Hydraulic Conductivity of Gravels Using a Laboratory Permeameter and Silty Sands Using Field Testing with Observation Wells" (2013). Dissertations. 746. http://scholarworks.umass.edu/open_access_dissertations/746