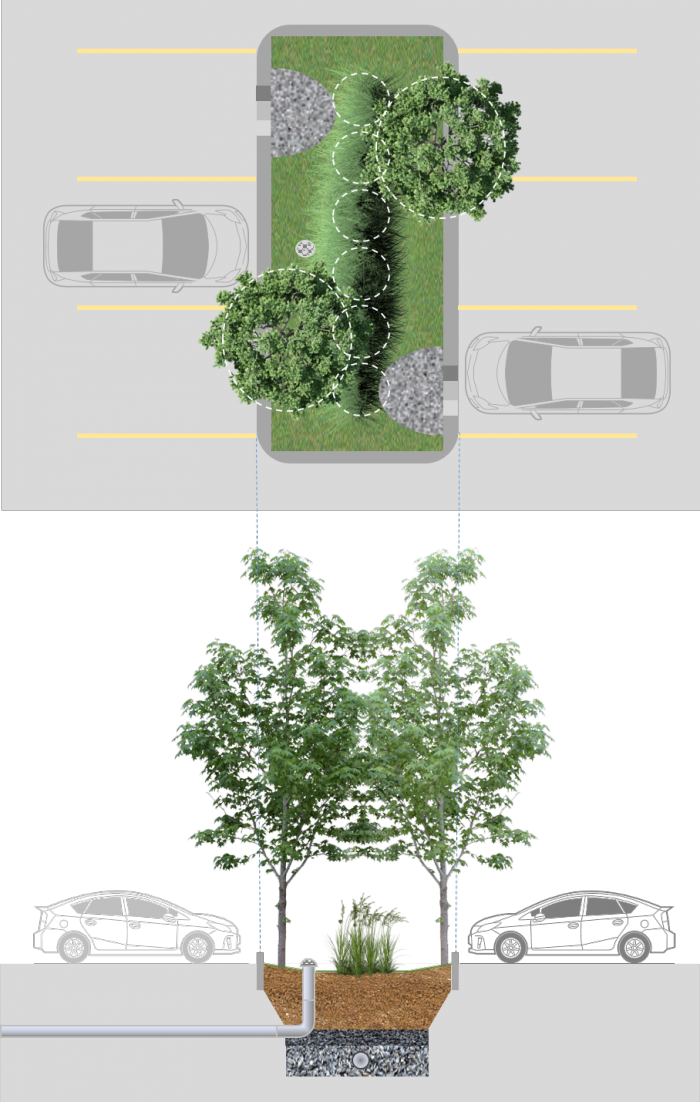
Bioretention: Parking lots
On commercial, industrial and multi-unit developments, a popular choice is to integrate bioretention into parking lot landscaped areas. These distributed cells typically accept sheet flow through multiple curb cuts, have shallow depression storage ≤ 100 mm, and a total area of 5 -200 m2. Although many parking lot schemes include long linear bioretention cells (≥ 0.6 m wide), infiltration is optimized by having a level grade and a level base, unlike a bioswale.
Winter maintenance[edit]
Salt can be damaging to the planting in parking lot bioretention. To help minimize this, bioretention practices adjacent to parking areas should always have an underdrain and salt use be reduced through good design and planning of the parking lot.
Gallery[edit]
Parking lot bioretention with inspection well in foreground, Kortright centre, Vaughan
Parking lot bioretention with decorative stone for erosion control, and inspection well in foreground, Earth rangers, Vaughan
The sunken curb holds the edge of the asphalt pavement and lets water freely flow to the bioretention cell beside the 7sigma parking lot in Minneapolis, MN (USA)
Photo credit:BrianAshBioretention cells on Elm Drive, Mississauga, are lower then the adjacent road to accommodate a catch basin inlet between the paved surface and the cells.