Difference between revisions of "Source Water Protection"
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
A Wellhead Protection Area (WHPA) is an area located on the ground surface that denotes a specific zone within a known aquifer where fresh groundwater flows to a pumping well. Any detrimental activities/actions that take place in this zone may contribute to pollutions that can infiltrate into the underlying soil below and in turn contaminate said groundwater source for private and municipal wells alike - hence undertaken in this area may release pollutants that could seep into the soil and contaminate the groundwater used by both domestic and municipals wells. As a result, these areas require high levels of monitoring, protection and enforcement. Accordingly, this area warrants greater protection. | A Wellhead Protection Area (WHPA) is an area located on the ground surface that denotes a specific zone within a known aquifer where fresh groundwater flows to a pumping well. Any detrimental activities/actions that take place in this zone may contribute to pollutions that can infiltrate into the underlying soil below and in turn contaminate said groundwater source for private and municipal wells alike - hence undertaken in this area may release pollutants that could seep into the soil and contaminate the groundwater used by both domestic and municipals wells. As a result, these areas require high levels of monitoring, protection and enforcement. Accordingly, this area warrants greater protection. | ||
The risk to groundwater quality at the well site is determined by the rate at which a specific pollutant/contaminant can infiltrate and travel to the well and the time it would take to remediate the contaminant from the water supply by trained municipal water operators. | The risk to groundwater quality at the well site is determined by the rate at which a specific pollutant/contaminant can infiltrate and travel to the well and the time it would take to remediate the contaminant from the water supply by trained municipal water operators. If a chemical/contaminant spill were to happen a far distance away from a known well, a follow up assessment will be required, this assessment includes: | ||
* Determining whether the contaminant could reach the well in question and the duration of time it may take to reach it. | |||
* Is the contaminant a human, biological or environmental risk or is it simply an aesthetic nuisance? | |||
* Will the concentration of said contaminant exceed the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (CWQG) for drinking water standard or the Provincial Water Quality Network's (PWQMN) standard (i.e. [[Salt#Guidelines|chloride levels]])? | |||
* Will the current mitigation/treatment protocols currently used be sufficient enough to mitigate/remove the harmful concentration levels of said contaminant from reaching the well? | |||
** If said mitigation/treatment protocol needs to be amended and time allows a mitigation system can be installed to limit the movement of said chemical to the well or the water treatment process at the receiving Water Treatment Plant (WTP) can be modified to sufficiently decrease the concentrations being received | |||
When it comes to WHPAs once size does not fit all, there are multiple zones that extend in an irregular radius around a well to ensure adequate protection of the source water protection area, which is divided into five (5) zones based upon contaminant travel time within groundwater sources: | |||
'' | {{textbox: | ||
# '''WHPA-A''' – an area of 100 metre radius around the wellhead | |||
# '''WHPA-B''' – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between two years and the 100 metre distance | |||
# '''WHPA-C''' – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between five and two years | |||
WHPA-A – an area of 100 metre radius around the wellhead | # '''WHPA-D''' – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between 25 and five years | ||
WHPA-B – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between two years and the 100 metre distance | # '''WHPA-E''' – the area on ground surface through which surface water flows in two hours to a point close to the well. This wellhead protection area is only delineated when studies have shown that surface water can relatively easily seep through the soil and impact the quality of the water at the well. This situation is known as groundwater under the direct influence of surface water, or a GUDI well}} (Halton-Hamilton Source Protection Region, 2010<ref>Halton-Hamilton Source Protection Region. 2010. Wellhead Protection Areas (WHPAs). Planning Process - Vulnerable Areas. Accessed 02 June 2022. http://protectingwater.ca/planning.cfm?smocid=1440&parentcatid=841#:~:text=A%20wellhead%20protection%20area%20(WHPA,both%20domestic%20and%20municipals%20wells.</ref>; | ||
WHPA-C – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between five and two years | |||
WHPA-D – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between 25 and five years | |||
WHPA-E – the area on ground surface through which surface water flows in two hours to a point close to the well. This wellhead protection area is only delineated when studies have shown that surface water can relatively easily seep through the soil and impact the quality of the water at the well. This situation is known as groundwater under the direct influence of surface water, or a GUDI well | |||
====Intake Protection Zones (IPZs)==== | ====Intake Protection Zones (IPZs)==== | ||
Revision as of 13:49, 2 June 2022
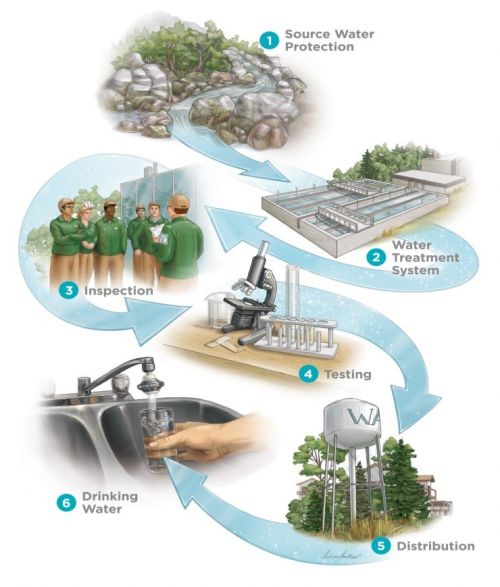
Overview[edit]
Spurred mainly by the Walkerton Tragedy in May of 2000, where 2,500 residents of the town fell ill due to ingesting high levels of E.coli bacteria and 7 individuals died due to poor monitoring and maintenance of the drinking water system, the province (Scarfone, 2020)[2] took major overhauling actions to ensure Ontarians drinking water was adequately protected.
Following an inquiry into the Walkerton event, Justice, O'Connor at the time made over 120 recommendations to better protect the province's drinking water, which have now been implemented and are the foundation of the province's drinking water protection framework. The first of these recommendations was that drinking water should be protected by developing watershed-based source water protection plans, which have been in place since 2006 with the adoption of the Clean Water Act (Government of Ontario, 2021)[3]
Source Water Protection in Ontario[edit]
Since the Clean Water Act, 2006 was adopted within the province the original recommendations of the "Walkerton Inquiry" were able to begin to be implemented. The legislation required municipalities protect their drinking water sources and supplies through prevention by developing collaborative large-scale watershed-based source protection plans or source water protection (SWPP) based on monitoring results and the latest science. When the Clean Water Act was first established the province paid for the cost of developing the preliminary SWPPs.
Under the Clean Water Act the legislation describes newly developed source water protection areas and source water protection regions.
- Source Protection Region (SPR): Encompass one or more source protection areas (ex. Credit Valley-Toronto and Region-Central Lake or simply the CTC Region).
- Source Protection Area (SPA): Smaller geographic areas generally based on the watershed boundaries of Ontario's 36 Conservation Authorities
Under the Clean Water Act local multi-stakeholder source protection committees were developed for each region. Each committee is comprised on the region's leading researchers, professionals and technical personnel that help identify significant current and potential future threats to their local municipal drinking water sources. Their job is to regularly meet and develop preventative plans to address identified and theorized threats (Lake Erie Source Protection Region, 2022)[5]
Source Protection Plans (SPP)[edit]
Source protection plans (SPPs) contain a number of policies that are locally developed by their local technical committees aimed at protecting existing and future spruces of adequate drinking water sources for impacted municipalities.
The associations who are reporting and implementing SPP policies and progress annually include:
- Conservation Authorities;
- Municipalities;
- Source protection authorities;
- Local health boards;
- Indigenous groups, committees and governments;
- Local businesses
- The Province of Ontario; and,
- Others (Government of Ontario, 2021)[3]
The Source Protection Committee generally uses varied approaches to protect drinking water sources within each SPR/SPA, which can include:
- Prescribed policy instruments (existing provincial approvals such as Environmental Compliance Approvals and Permits To Take Water);
- Requiring any owners/developers present a formalized risk management plan (negotiated individually);
- Specified land use planning;
- Prohibition of activities that may prove detrimental to SPZs; and/or,
- Current outreach and education activities (webinars, town meetings, pamphlets, online education hubs) (CTC SPR, 2019)[6]
Under the Clean Water Act, 2006 a total of 19 SPRs and SPA's have been established across the province. Each of these 19 SPRs/SPAs contain their own local multi-stakeholder source protection committees across the province which have developed 38 local source protection plans. These specialized plans identify various actions to protect over 450 affected municipal drinking water systems (covering 95% of Ontario's population) (Government of Ontario, 2021)[3].
Ultimately, SPPs are plans to help reduce or eliminate significant drinking water threats within its associated zone/area. These drinking water threats are listed in the following and the SPPS have policies place which must also be enforced. These policies when implemented help to both manage and/or prohibit significant threats as a result of various activities to ensure that they cannot pollute or deplete necessary sources of municipal drinking water within the zone/area.

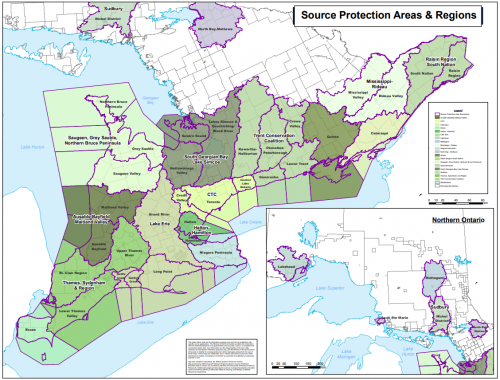
SPRs & SPAs in Ontario[edit]
Listed below are 19 different SPRs and SPAs in Ontario, where you can visit each Region's/Area's dedicated Sourcewater protection website for information on their committee members, recent reports, helpful documents, informational videos and the like:
- Ausable Bayfield Maitland Valley Source Protection Region
- Cataraqui Source Protection Area
- CTC Source Protection Region
- Essex Region Source Protection Area
- Greater Sudbury Source Protection Area
- Halton-Hamilton Source Protection Region
- Lake Erie Source Protection Region
- Lakehead Source Protection Area
- Mattagami Region Source Protection Area
- Mississippi-Rideau Source protection Region
- Niagara Peninsula Source Protection Area
- North Bay-Mattawa Source Protection Area
- Quinte Region Source Protection Area
- Raisin-South Nation Source Protection Region
- Saugeen, Grey Sauble, Northern Bruce Peninsula Source Protection Region
- Sault Ste. Marie Region Source Protection Area
- South Georgian Bay Lake Simcoe Source Protection Region
- Thames-Sydenham Source Protection Region
- Trent Conservation Coalition Source Protection Region
Source Protection Assessment Reports[edit]
Each of the 19 aforementioned SPRs & SPAs has an Assessment Report that acts as a 'living technical document' for that given region. The Assessment report includes:
- Recent research findings and scientific information regarding source water protection;
- A brief overview of each impacted watershed within the SPR/SPA;
- Provides a water budget (which is a way to measure the amount of freshwater water enters, is stored, and leaves a watershed);
- Identifies vulnerable areas near key freshwater sources (municipal wells and intakes);
- Identifies the number of significant threats (agricultural practices, sewage sources, fertilizers, etc.) to water quality near wells and intakes; and,
- Identifies areas that could have varied threat levels (low, moderate, high) (CTC SPR, 2019)[6]
Planning Considerations[edit]
Inclusion of the tools and atlas
- Recommendations - refer to SPP (pull from B.C's recommended practices)
- Top lessons and maintenance (setback distances / replacing media)
Talk about pretreatment - filtration before being sent directly to groundwater source (bioretention/swale -> infiltration trench) Online vaults from minor system flows (filter and target specific pollutants) - before infiltration.
When planning any new development within a SPR/SPA its important to follow the following four (4) major Steps before moving forward.
1) Identify and Map Vulnerable Areas[edit]
The two major areas of significance that are vulnerable to water/groundwater pollution threats are called Wellhead Protection Areas (WHPAs) and Intake Protection Zones (IPZs). New development must note if any of their proposed activities or future actions will cause potential negative impacts on these important municipal sources of freshwater.
Wellhead Protection Areas (WHPAs)[edit]
A Wellhead Protection Area (WHPA) is an area located on the ground surface that denotes a specific zone within a known aquifer where fresh groundwater flows to a pumping well. Any detrimental activities/actions that take place in this zone may contribute to pollutions that can infiltrate into the underlying soil below and in turn contaminate said groundwater source for private and municipal wells alike - hence undertaken in this area may release pollutants that could seep into the soil and contaminate the groundwater used by both domestic and municipals wells. As a result, these areas require high levels of monitoring, protection and enforcement. Accordingly, this area warrants greater protection.
The risk to groundwater quality at the well site is determined by the rate at which a specific pollutant/contaminant can infiltrate and travel to the well and the time it would take to remediate the contaminant from the water supply by trained municipal water operators. If a chemical/contaminant spill were to happen a far distance away from a known well, a follow up assessment will be required, this assessment includes:
- Determining whether the contaminant could reach the well in question and the duration of time it may take to reach it.
- Is the contaminant a human, biological or environmental risk or is it simply an aesthetic nuisance?
- Will the concentration of said contaminant exceed the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (CWQG) for drinking water standard or the Provincial Water Quality Network's (PWQMN) standard (i.e. chloride levels)?
- Will the current mitigation/treatment protocols currently used be sufficient enough to mitigate/remove the harmful concentration levels of said contaminant from reaching the well?
- If said mitigation/treatment protocol needs to be amended and time allows a mitigation system can be installed to limit the movement of said chemical to the well or the water treatment process at the receiving Water Treatment Plant (WTP) can be modified to sufficiently decrease the concentrations being received
When it comes to WHPAs once size does not fit all, there are multiple zones that extend in an irregular radius around a well to ensure adequate protection of the source water protection area, which is divided into five (5) zones based upon contaminant travel time within groundwater sources:
{{textbox:
- WHPA-A – an area of 100 metre radius around the wellhead
- WHPA-B – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between two years and the 100 metre distance
- WHPA-C – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between five and two years
- WHPA-D – the zone through which it takes groundwater to travel between 25 and five years
- WHPA-E – the area on ground surface through which surface water flows in two hours to a point close to the well. This wellhead protection area is only delineated when studies have shown that surface water can relatively easily seep through the soil and impact the quality of the water at the well. This situation is known as groundwater under the direct influence of surface water, or a GUDI well}} (Halton-Hamilton Source Protection Region, 2010[8];
Intake Protection Zones (IPZs)[edit]
2) Identify Threats[edit]
3) Calculate Threat Level[edit]
4) Apply Appropriate Policies[edit]
Site Considerations[edit]
| Installation type | Depth to high water or bedrock (m)i | Ratio of impervious drainage area to permeable facility footprint area |
Native soil infiltration rate (mm/hr)ii | Head (m)iii | Space %iv | Slope %v | Applicable in pollution hotspotsvi | Set backs | Karstvii | Drinking Water Source Protection wellhead protection area time of travel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rain barrels | Not a constraint | Not applicable | Not a constraint | 1 | 0 | NA | Yes | None | Yes | None |
| Cisterns | Not a constraint | Not applicable | Not a constraint | 0 | 0 | 0 | Yes | None | Yes | None |
| Roof downspout disconnection | Not a constraint | 4:1 or less | Decompaction if < 15 mm/hr | 0.5 | 5 to 20 | 1 to 5 | Yes | Building Foundation | Yes | None |
| Infiltration trenches or Infiltration chambers | 1 | 5:1 to 20:1 | Not a constraint | 1 to 2 | 0 to 1 | <15 % | Noix | 4m- Building Foundation Underground Utilities, Trees, Drinking Water Wellhead Protection Areas |
No | 2 yr |
| Bioretention | 1 (infiltrating); Not a constraint (non-infiltrating) | 5:1 to 15:1 | Decompaction and underdrain recommended if < 15 mm/hr (infiltrating) |
1 to 2 | 5 to 10 | 0 to 2 | No (infiltrating)ix; Yes (non-infiltrating) | 4m- Building Foundation Underground Utilities, Trees, Drinking Water Wellhead Protection Areas |
No (infiltrating); Yes (non-infiltrating) | 2 yr (infiltrating); None (non-infiltrating) |
| Stormwater planters | Not a constraint | 5:1 | Not a constraint | 1 to 2 | 2 to 5 | 0 to 2 | No (infiltrating)ix; Yes (non-infiltrating) | Building Foundation, Trees | No (infiltrating); Yes (non-infiltrating) | 2 Yr (infiltrating); None (non-infiltrating) |
| Vegetated filter strips | Not a constraint | 4:1 or less | Decompaction if < 15 mm/hr | 0 to 1 | 15 to 20 | 1 to 5 | Noix | None | Yes | None |
| Permeable pavements | 1 (infiltrating); Not applicable (non-infiltrating) | 0 to 1:1 | Underdrain recommended if < 15 mm/hr (infiltrating) |
0.5 to 1 | 0 | 1 to 5 | No (infiltrating)ix; Yes (non-infiltrating) | 4m-Underground Utilities Drinking Water Wellhead Protection Areas |
No (infiltrating); Yes (non-infiltrating) | 2 Yr (infiltrating); None (non-infiltrating) |
| Enhanced swales (featuring check dams) | 1 | 5:1 to 10:1 | Decompaction if < 15 mm/hr | 1 to 3 | 5 to 15 | 0.5 to 6 | Noix | 4m- Building Foundation Underground Utilities |
No | 2 Yr |
| Bioswales (Dry swales) | 1 (infiltrating); Not applicable (non-infiltrating) | 5:1 to 15:1 | Decompaction and underdrain recommended if < 15 mm/hr (infiltrating) |
1 to 3 | 5 to 10 | 0.5 to 6 | No (infiltrating)ix; Yes (non-infiltrating) | 4m (3m if impermeable liner is used) Building foundation, Underground utilities, Drinking Water Wellhead Protection Areas |
No (infiltrating); Yes (non-infiltrating) | 2 Yr (infiltrating); None (non-infiltrating) |
| Exfiltration trenches | 1 | 5:1 to 10:1 | Not a constraint | 1 to 3 | 0 | < 15% | Noix | 4m- Building Foundation Underground Utilities, Trees, Drinking Water Wellhead Protection Areas |
No | 2 Yr |
| Stormwater tree trenches | 1 | 5:1 to 15:1 | Underdrain recommended if < 15 mm/hr |
1 to 2 | 5 to 10 | 0 to 2 | Noix | 4m- Building Foundation Underground Utilities, Drinking Water Wellhead Protection Areas |
No | 2 yr |
| Notes |
|---|
| i Minimum depth between the base of the facility and the elevation of the seasonally high water table or top of bedrock |
| ii Infiltration rate estimates based on measurements of hydraulic conductivity under field saturated conditions at the proposed location and depth of the practice |
| iii Vertical distance between the inlet and outlet of the LID practice |
| iv Percent of open pervious land on the site that is required for the LID practice |
| v Slope at the LID practice location |
| vi Suitable in pollution hot spots or runoff source areas where land uses or activities have the potential to generate highly contaminated runoff |
| vii Suitability in areas of karst geologic formations |
| viii Drinking Water Source Protection wellhead protection area time of travel |
| ix May be allowed under special circumstances and if appropriate mitigation actions are taken - please contact your local Source Protection Region (SPR) or Source Protection Area (SPA) for further information. You can find your associated SPR/SPA based on your location here and then visit their site here |
Site Specific Jurisdictions[edit]
Source Water Protection Nationally[edit]
Nova Scotia[edit]
British Columbia (B.C)[edit]
Pretreatment Features[edit]
Design Features[edit]
LID BMPs
References[edit]
- ↑ Conservation Ontario. 2022. Best Practices for Source Water Protection. Accessed 27 May 2022: https://conservationontario.ca/conservation-authorities/source-water-protection/
- ↑ Scarfone, K. 2020. 20 years after the Walkerton Tragedy, Ontario could be setting itself up for a new water crisis. Safeguarding Freshwater. Environmental Defence. 1 June 2020. Accessed 26 May 2022. https://environmentaldefence.ca/2020/06/01/walkerton-tragedy-ontario-new-water-crisis/
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 Government of Ontario. 2021. Source protection. Environment and Energy - Drinking Water. 13 October 2021. Accessed: 26 May 2022. https://www.ontario.ca/page/source-protection#section-0
- ↑ Conservation Ontario. 2016. Protecting Our Sources of Drinking Water: Implementation of Source Protection Plans across Ontario. Written by: Chitra Gowda, 11 Oct. 2016. Accessed 27 May 2022: https://ijc.org/en/protecting-our-sources-drinking-water-implementation-source-protection-plans-across-ontario
- ↑ Lake Erie Source Protection Region. 2022. The Clean Water Act. Accessed 26 May 2022. https://www.sourcewater.ca/en/how-it-works/The-Clean-Water-Act.aspx
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 Credit Valley-Toronto and Region-Central Lake Ontario (CTC) Source Protection Region (SPR). 2019. Protecting our Drinking Water Sources. Accessed 26 May 2022. https://ctcswp.ca/app/uploads/2019/06/DOC_20190328_Magazine_DigitalSpreads_FNL.pdf
- ↑ Conservation Ontario. 2018. SWP Education & Outreach - Road Signage (English). Accessed 31 May 2022. https://conservationontario.ca/resources?tx_fefiles_files%5Baction%5D=show&tx_fefiles_files%5Bcontroller%5D=File&tx_fefiles_files%5Bfile%5D=389&cHash=88b06a201529f054e0a87582376f6c2a
- ↑ Halton-Hamilton Source Protection Region. 2010. Wellhead Protection Areas (WHPAs). Planning Process - Vulnerable Areas. Accessed 02 June 2022. http://protectingwater.ca/planning.cfm?smocid=1440&parentcatid=841#:~:text=A%20wellhead%20protection%20area%20(WHPA,both%20domestic%20and%20municipals%20wells.